NEWS, EVENTS & BLOG
BLOG

Is a Headless Computer Right for Your Application?
Press Office, VersaLogic Corporation, 04/22/21
Part One: When Power is Limited
Embedded / industrial single board computers (SBCs) come in a variety of sizes, shapes, performance levels and functionality. In most cases, they include connectivity to human machine interface (HMI) devices such as keyboards, mice, and displays.
However, in some use cases HMI functions are not required and in others it might even be detrimental. One that comes immediately to mind is in systems where power supply capacity is limited. That use case is the subject of this blog. A subsequent blog will address the case of edge servers where direct HMI connections are not required.
The term “headless” is used to describe an SBC that has no HMI connectivity. Usually, there is no display connector. USB connections usually remain as they can be used for connection to other I/O devices.
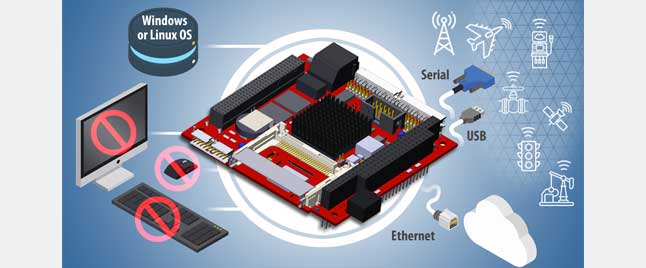 Attributes of a headless SBC
Attributes of a headless SBC
When dealing with power-constrained systems, a headless single board computer can provide a significant power saving. For example, VersaLogic’s headless Tomcat has a typical power consumption of 3W, which compares favorably with 7W typical for similar X86 boards that include a display output.
 The power-frugal PC/104 Tomcat
The power-frugal PC/104 Tomcat
Headless applications fall into two categories:
- Remote installations where there is not usually an operator or other human interaction
- Systems where the computing is distributed by function
Metering data collection systems for utilities are an example of the former. The systems include tower gateway base stations for data collection. In normal operation, these base stations are supervised remotely and so a headless SBC, such as Tomcat, fits the bill.
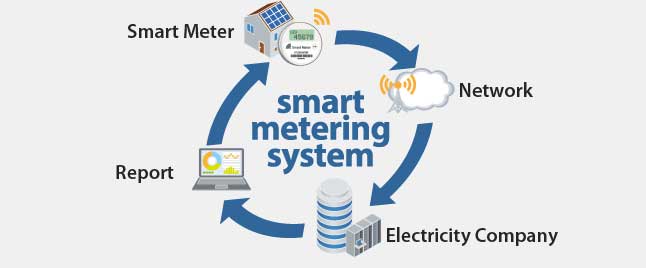 Data collection is a key part of smart metering systems
Data collection is a key part of smart metering systems
The need for a headless SBC is less obvious in an application where there will be direct human interaction. However, in many of these applications, the embedded computing functions are divided. An example of this is a phacoemulsification device used in cataract surgery. In this and other medical applications, there is a dedicated HMI SBC and a second headless SBC that is running mechanical manipulators and fluid pumps and valves.
There are also defense applications where a headless SBC provides the ideal solution. For example, in military software-defined radio systems (SDR) there may be central switching units that are not part of the direct interface with users. The headless Tomcat is currently being deployed in such a tactical communications system.
 SDR central switch does not need local HMI
SDR central switch does not need local HMI
When HMI is needed – System Development and Debug
Although not required or desired in a deployed system, there may still be a need for HMI connectivity during system development or debug. As mentioned earlier, headless SBCs will usually have USB ports, so connection of a keyboard and mouse is not a problem.
However, a display is still needed. For an SBC such as the Tomcat, the answer is to use its PC/104-plus expansion capability. PC/104 video expansion cards such as the EPM-V7 can be temporarily plugged in when a display connection is required. For headless SBCs that include mini PCIe sockets, a video card such as the MPEe-V5 is the answer.
 PC/104-plus EPM-V7 and mini PCIe MPEe-V5 video expansion cards
PC/104-plus EPM-V7 and mini PCIe MPEe-V5 video expansion cards
In Closing
In conclusion, with a headless SBC you can have the best of both worlds: a low power draw in a deployed system and the ability to use add-on video expansion during system development.
Look for a future blog where headless edge-deployed micro-servers will be discussed.
Need additional Information?
Want to know more about VersaLogic’s range of embedded products? Let’s start a conversation.
